🐧 Linux
A Postgres database with a user and password and sufficient permissions to create schemas in the database must be ready before proceeding with the installation.
If you need help to install and configure the Postgres database server please visit the Advanced Topics -> Postgres section.
1. Debian based distributions
The OpenUEM server components can be installed on a Debian 12/Ubuntu 24.04 machine using .deb packages available in OpenUEM repository.
1.1 Adding the repository
The Debian/Ubuntu repository and its contents are signed with a GPG public key
To download the public GPG key and add it to the keyring use the following command:
sudo apt install -y curl
curl -fsSL https://apt.openuem.eu/pgp-key.public | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/openuem.gpg
Now, to add the repository, run the following command:
For amd64 architecture:
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/openuem.gpg] https://apt.openuem.eu stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/openuem.list
For arm64 architecture:
echo "deb [arch=arm64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/openuem.gpg] https://apt.openuem.eu stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/openuem.list
Update the repositories:
sudo apt update -y
1.2. Install OpenUEM server
Start the installation running:
sudo apt install -y openuem-server
You'll have to answer some questions about configuration
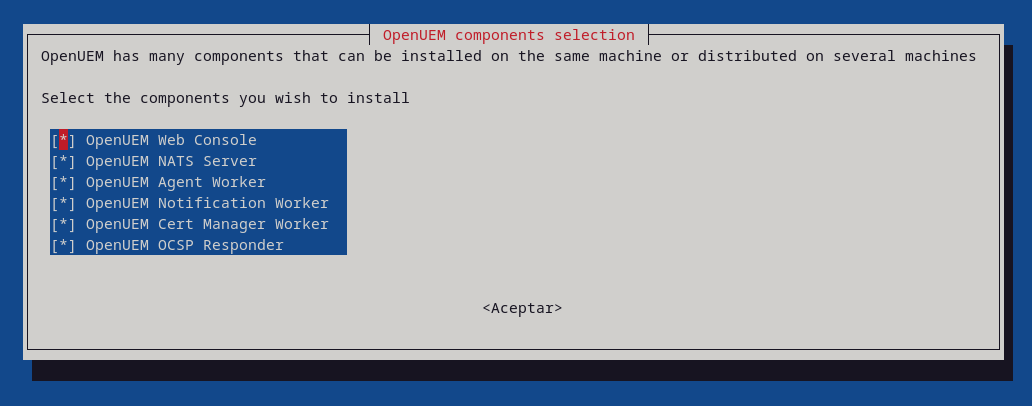
This page shows information about the simplest path to installing all OpenUEM components in the same machine. If you prefer to install components on different machines different questions will be asked associated with the component being installed
Select the components that you want to install (press the space bar to toggle selection)
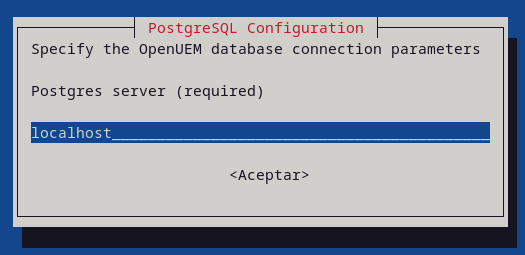
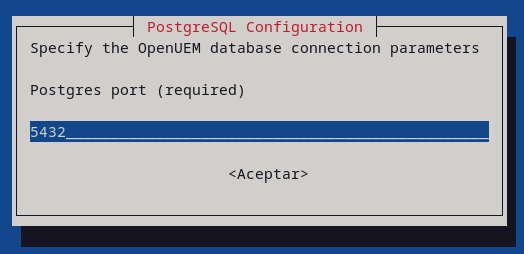
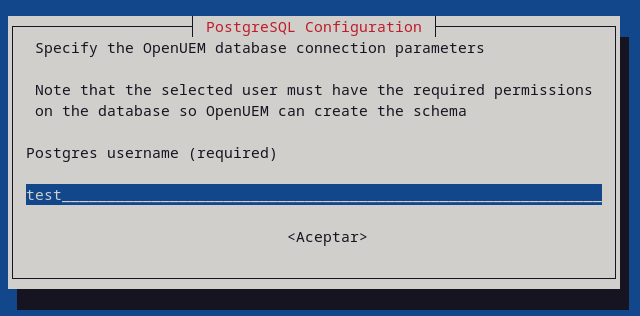
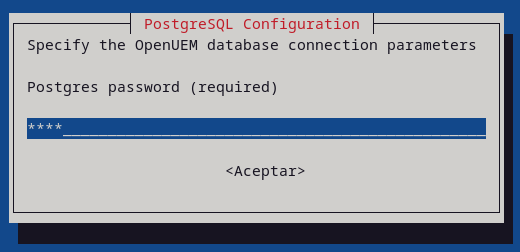
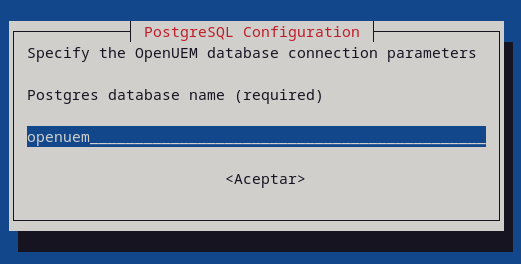
Now, specify the OpenUEM database connection parameters (host, port, user, password and database name)
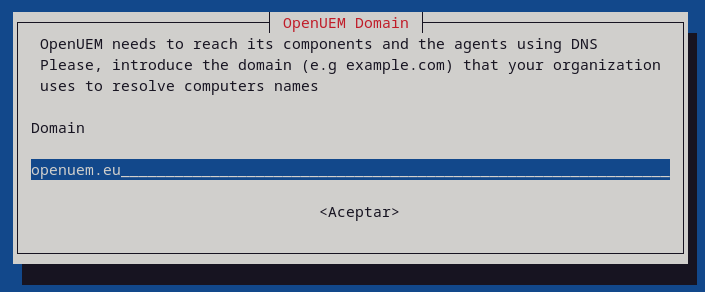
OpenUEM needs a DNS domain for your organization to resolve agent/endpoint names to IP address. Set the domain name to be used
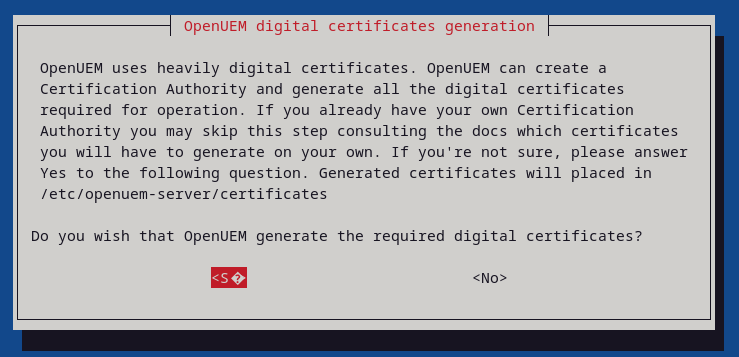
OpenUEM uses digital certificates to establish secure communication and TLS certificates. Unless you're using your own Certificate Authority, answer yes to this question so OpenUEM creates a Certificate Authority and the required certificates.
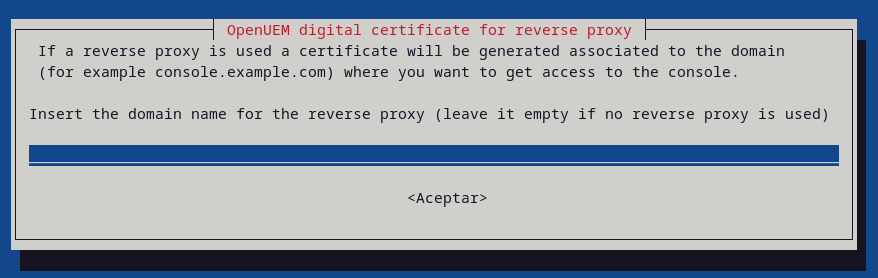
If you want to use OpenUEM behind a reverse proxy, set the DNS name that you want to use to access OpenUEM console
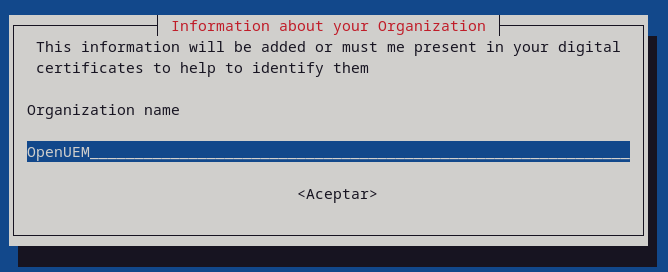
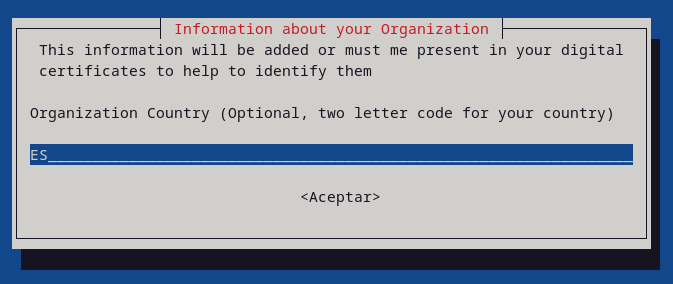
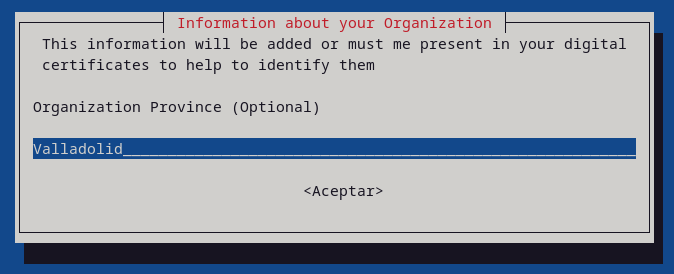
Now, you'll have to answer a few questions about your organization. These answers are only used to set values that identify your digital certificates and authenticate your NATS server connection.
It’s time to specify which domain name and port will be used by the NATS server:
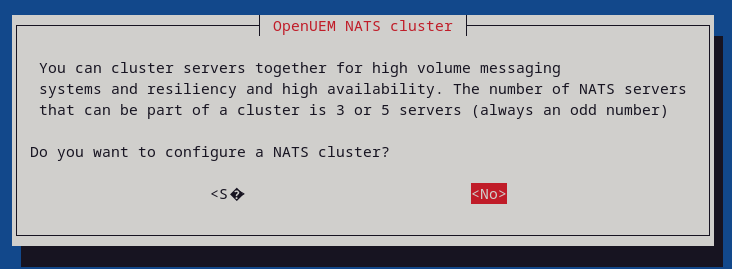
If you want to use a NATS cluster, answer Yes to the question. If it's the first time you install OpenUEM or you're not using hundreds of agents, it's better to answer No.
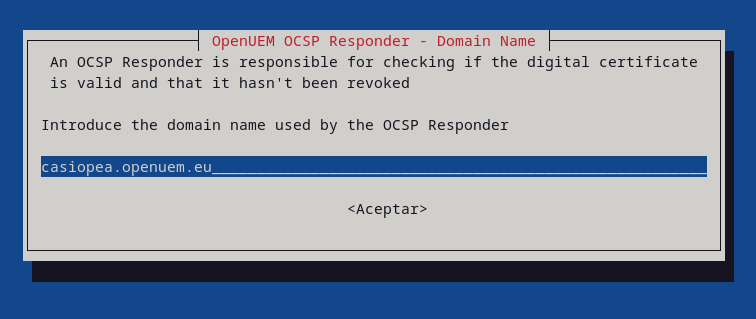
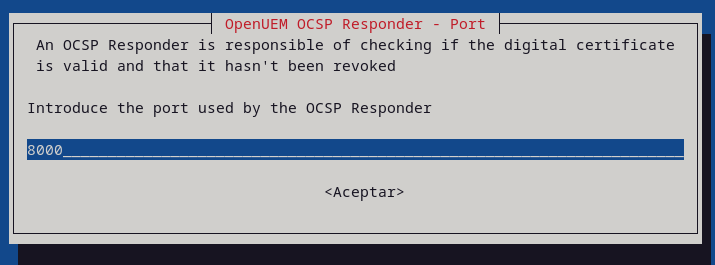
Introduce the domain name and the port used by the OCSP Responder
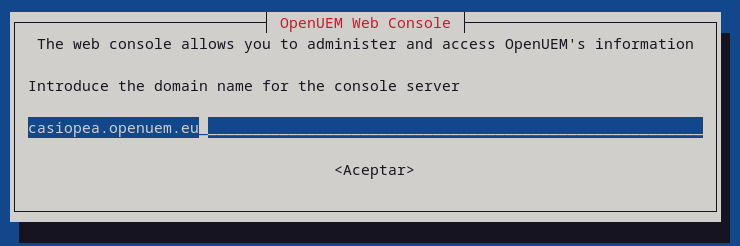
You'll have to specify the DNS domain name used by the server that hosts the console service, and the ports used by the web server and the authentication server.
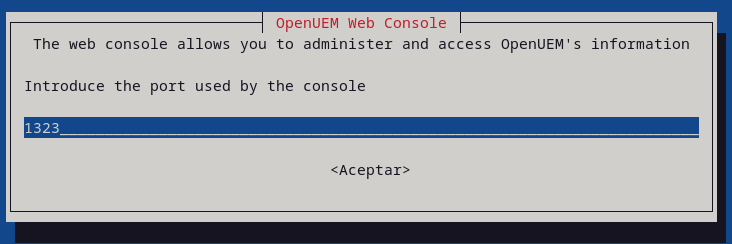
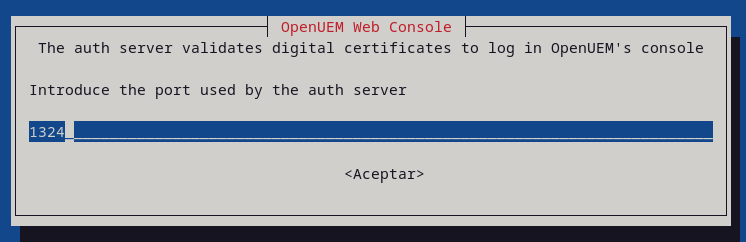
If you want to use OpenUEM behind a reverse proxy you must specify the domain name associated with the console service (unless you're letting OpenUEM generate the certificates and have already specified the DNS domain name), and the port used by the reverse proxy to run the authentication service.
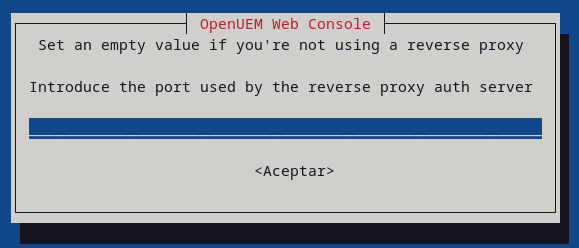
The console uses a key to encrypt tokens, please set a complex key (and confirm it in the following question)
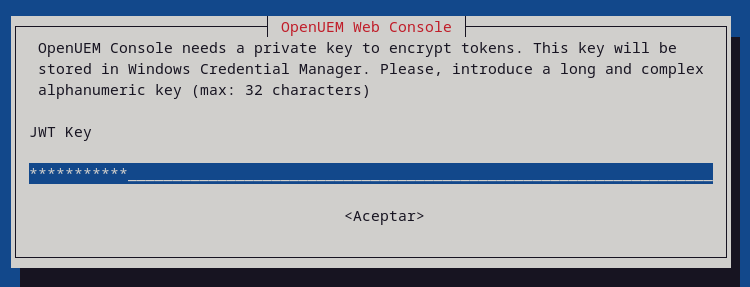
If OpenUEM has been selected to generate certificates automatically you've the chance to specify the password that protects the admin user certificate, and the system's username associated with the certificate, so the certificate can be added to this user's browsers certificate store.
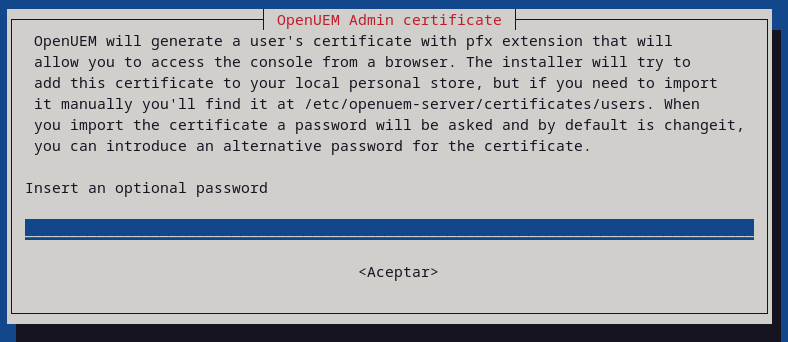

Once, all the questions are answered the package will be installed.
Installation may take some minutes if it must generate certificates so if you see that progress stalls for some minutes (generally at 60% or 80%), please be patient as cryptographic operations are heavy, database schema is created, and hundreds of megabytes are copied.
A user openuem will be created during the installation. Only this unprivileged user (or root user, of course) will have access to the config file, digital certificates and logs.
After the installation finishes, you'll see the following message:
2. RedHat based distributions
The OpenUEM server components can be installed on a RedHat based distributions like Fedora, Alma Linux and Rocky Linux using .rpm packages available in OpenUEM repository.
2.1 Adding the repository
The RPM repository and its contents are signed with a GPG public key
To add the repository, run the following command:
sudo bash -c 'echo "[openuem]
name=OpenUEM
baseurl=https://rpm.openuem.eu/packages
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://rpm.openuem.eu/pgp-key.public" > /etc/yum.repos.d/openuem.repo'
2.2 Install OpenUEM components
The OpenUEM RPM repository has packages for every component and tool required to run an OpenUEM server:
- openuem-console
- openuem-ocsp-responder
- openuem-nats-service
- openuem-agent-worker
- openuem-cert-manager-worker
- openuem-notification-worker
- openuem-server-updater
- openuem-cert-manager
openuem-server-updater requires a package called crudini that may not be available in your distribution's default repositories. If installation fails, you may have to add the EPEL repository. For example, in Alma Linux, run dnf install epel-release so the crudini package can be found in the EPEL repository.
You can install these components in different machines, if you want OpenUEM to run in a distributed mode, or install them all on the same machine.
For example:
sudo dnf install -y openuem-console
sudo dnf install -y openuem-ocsp-responder
sudo dnf install -y openuem-nats-service
sudo dnf install -y openuem-agent-worker
sudo dnf install -y openuem-cert-manager-worker
sudo dnf install -y openuem-notification-worker
sudo dnf install -y openuem-server-updater
sudo dnf install -y openuem-cert-manager
The first time you install packages from OpenUEM's repository you'll have to accept the GPG key
In any machine that hosts a OpenUEM component you must install the openuem-server-updater package
2.3 Configure OpenUEM
Once you install the packages, you’ll have to perform some or all of the following configuration steps.
2.3.1 Create OpenUEM certificates
If you don’t own your own Certificate Authority (CA) you’ll have to create a CA and generate certificates for all the components. The openuem-cert-manager tool (installed by the package with the same name) can be used to perform those tasks, but you may use tools like Cloudflare’s CFSSL to generate them.
Before you use the openuem-cert-manager tool you should create the following environment variables:
- ORGNAME: the name of your organization
- COUNTRY: two-letter country code of the country where your organization is located (ISO 3166)
- ORGPROVINCE: the province where your organization is located
- ORGLOCALITY: the locality where your organization is located
- ORGADDRESS: the address of your organization
- DATABASE_URL: the URL to connect with your database postgres://user:password@localhost:5432/openuem
- NATS_SERVER: the hostname of the server that contains the NATS service
- OCSP_SERVER: the hostname of the server that contains the OCSP Responder service
- OCSP_PORT: the port that will be used for the OCSP Responder service
- CONSOLE_SERVER: the name of the server that contains the console service
If you're going to host the console service behind a reverse proxy you'll have to create a variable to store the hostname that you want to use. You'll have to add the certificate that you generate to your reverse proxy configuration.
- REVERSE_PROXY_SERVER
For example:
export ORGNAME=OpenUEM
export COUNTRY=ES
export ORGPROVINCE=Valladolid
export ORGLOCALITY=Valladolid
export ORGADDRESS="Fake St 123"
export DATABASE_URL="postgres://test:test@localhost:5432/openuem"
export NATS_SERVER="terminus.openuem.eu"
export OCSP_SERVER="terminus.openuem.eu"
export OCSP_PORT=8000
export CONSOLE_SERVER="terminus.openuem.eu"
export REVERSE_PROXY_SERVER="console.openuem.eu"
Now let's create the /etc/openuem-server/certificates folder where OpenUEM will search for certificates
sudo mkdir -p /etc/openuem-server/certificates/{ca,nats,ocsp,notification-worker,agents-worker,cert-manager-worker,console,updater,agents,users}
sudo chown -R openuem:openuem /etc/openuem-server/certificates/
cd /etc/openuem-server/certificates
If you want to use a different path, you can change the paths to certificates in the /etc/openuem-server/openuem.ini configuration file inside the Certificates section
It's time to create the CA
sudo openuem-cert-manager create-ca --name "OpenUEM CA" --dst ./ca --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 10
You'll see an output like this:
2025/05/03 09:50:49 ... generating your CA certificate and private keys
2025/05/03 09:50:51 ... creating your CA certificate
2025/05/03 09:50:51 ... saving your CA certificate to ca/ca.cer
2025/05/03 09:50:51 ... saving your CA private key to ca/ca.key
2025/05/03 09:50:51 ✅ Done! Your CA certificate and private key has been stored in the certificates folder. Create a backup of these files and store them in a safe and secure place
Once the CA is generated, the certificate and the private key for the CA are ready to generate the rest of the certificates required by the components
NATS Service certificates:
sudo openuem-cert-manager server-cert --name "OpenUEM NATS" --dst ./nats --type="nats" --client-too --dns-names "$NATS_SERVER" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "nats" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --dburl "$DATABASE_URL" --description "NATS certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key
OCSP Responder certificates:
sudo openuem-cert-manager server-cert --name "OpenUEM OCSP" --dst ./ocsp --type="ocsp" --sign-ocsp --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "ocsp" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "OCSP certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Notification Worker certificates:
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM Notification Worker" --dst ./notification-worker --type="worker" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "worker" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Notification Worker's certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Agent Worker certificates:
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM Agent Worker" --dst ./agents-worker --type="worker" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "worker" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Agent Worker's certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Cert-Manager Worker certificates:
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM Cert-Manager Worker" --dst ./cert-manager-worker --type="worker" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "worker" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Cert-Manager Worker's certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Console certificates
You'll have to create a certificate for every console server that you want to use
sudo openuem-cert-manager server-cert --name "OpenUEM Console" --dst ./console --type="console" --client-too --dns-names "$CONSOLE_SERVER" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "console" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Console certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Console reverse proxy
Only if you want to have the console service with a reverse proxy and load balance the service
sudo openuem-cert-manager server-cert --name "OpenUEM Reverse Proxy" --dst ./console --type="proxy" --dns-names "$REVERSE_PROXY_SERVER" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "proxy" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Reverse Proxy certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
SFTP certificates
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM SFTP Client" --dst ./console --type="console" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "sftp" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "SFTP Client" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Server updater certificates
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM Updater Client" --dst ./updater --type="updater" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "updater" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Updater Client" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Agents certificates
sudo openuem-cert-manager client-cert --name "OpenUEM Agent" --dst ./agents --type="agent" --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --filename "agent" --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "Agent certificate" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
Admin certificate
Create the admin user client certificate and private key for console access.
sudo openuem-cert-manager user-cert --username admin --dst ./users --org "$ORGNAME" --country "$COUNTRY" --province "$ORGPROVINCE" --locality "$ORGLOCALITY" --address "$ORGADDRESS" --years-valid 2 --ocsp "http://$OCSP_SERVER:$OCSP_PORT" --description "OpenUEM Administrator" --cacert ./ca/ca.cer --cakey ./ca/ca.key --dburl "$DATABASE_URL"
If you need to re-run the previous command note that you must remove the admin user row from the table users of your database
2.3.2 Create the openuem.ini configuration file
All OpenUEM components use the /etc/openuem-server/openuem.ini configuration file. The openuem.ini file is created when the openuem-server-updater package is installed.
You’ll need to edit the openuem.ini file and set the following configuration entries depending on the components that you want to have on that server.
Components
Specify which components are installed on the server, uncommenting (removing the # at the start of the line) the entry for each component:
[Components]
NATS=yes
OCSP=yes
AgentWorker=yes
CertManagerWorker=yes
NotificationWorker=yes
Console=yes
DATABASE
For database connections, you have to set the following entries
[DB]
PostgresHost=localhost
PostgresPort=5432
PostgresUser=test
PostgresPassword=test
PostgresDatabase=openuem
PostgresUrl=postgres://test:test@localhost:5432/openuem
OCSP Responder
You have to specify the hostname and the port used by the service
[OCSP]
OCSPServer=terminus.openuem.eu
OCSPPort=8000
Cert Manager Worker
The following information is required so the Cert-Manager worker can generate certificates on demand
[Certificates]
OCSPUrls=http://terminus.openuem.eu:8000
OrgName=OpenUEM
OrgCountry=ES
OrgProvince=Valladolid
OrgLocality=Valladolid
OrgAddress=Fake St 123
Certificates
The following entries must be included un uncommented in the certificates section
CACert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/ca/ca.cer
CAKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/ca/ca.key
NATSCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/nats/nats.cer
NATSKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/nats/nats.key
OCSPCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/ocsp/ocsp.cer
OCSPKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/ocsp/ocsp.key
NotificationWorkerCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/notification-worker/worker.cer
NotificationWorkerKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/notification-worker/worker.key
CertManagerWorkerCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/cert-manager-worker/worker.cer
CertManagerWorkerKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/cert-manager-worker/worker.key
AgentWorkerCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/agents-worker/worker.cer
AgentWorkerKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/agents-worker/worker.key
ConsoleCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/console/console.cer
ConsoleKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/console/console.key
SFTPKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/console/sftp.key
UpdaterCert=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/updater/updater.cer
UpdaterKey=/etc/openuem-server/certificates/updater/updater.key
NATS Service
You must add the following if the NATS component is used in this server
[NATS]
NATSPort=4433
NATSServer=terminus.openuem.eu
Console Service
If you run the console service you must the hostname and the port used by the console and authentication servers. Then if you are using the console behind a reverse proxy, you must set the hostname for the reverse proxy server and the port that you'll set in the reverse proxy for authentication.
The reverseproxyserver and reverseproxyauthport must exist even if you're not using a reverse proxy. You should set an empty value for these properties
Also you have to set the domain name that you use in your organization and set a key for JWT tokens (32 byte max)
[Console]
hostname=terminus.openuem.eu
port=1323
authport=1324
reverseproxyserver=console.openuem.eu
reverseproxyauthport=1344
domain=openuem.eu
[JWT]
Key=averylongsecret
All components
The following must be added to the NATS section in any case:
NATSServers=terminus.openuem.eu:4433
2.3.3 Start the services
Now you must enable and start the services:
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-ocsp-responder
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-nats-service
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-server-updater
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-agent-worker
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-notification-worker
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-cert-manager-worker
sudo systemctl enable --now openuem-console
3. Next steps and troubleshooting
Once you install and configure OpenUEM it's time to visit the OpenUEM console in your browser.
Before you can access the console you must import the CA certificate and the admin user certificate using this instructions
Now open https://SERVER_NAME:CONSOLE_PORT (replace the values that you've set during the package configuration) and you should see OpenUEM's console
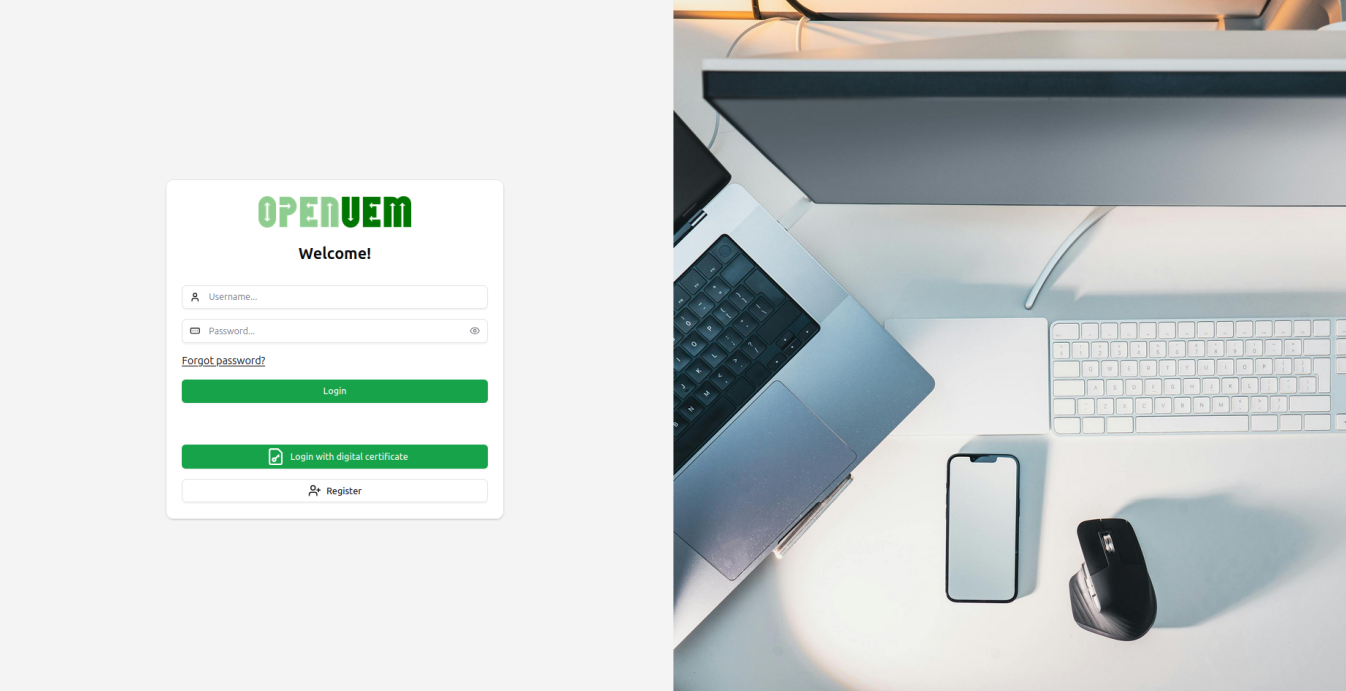
Finally, log in to the console
3.1 Services
OpenUEM will install and enable the following services on your server:
- openuem-agent-worker, see Workers for more information
- openuem-cert-manager-worker, see Workers for more information
- openuem-console, see Console for more information
- openuem-nats-service, see NATS for more information
- openuem-notification-worker, see Workers for more information
- openuem-ocsp-responder, see OCSP Responder for more information
- openuem-server-updater, that is responsible for updating the server components from the console
All OpenUEM services will be run under an unprivileged user account called openuem to mitigate risks. Also, these services have been prepared using sudo system-analyze securityto reduce exposure.
The only exception is the openuem-updater-service that requires higher privileges to reinstall OpenUEM components. There’s an open issue to reduce privileges and exposure.
3.2 Configuration
OpenUEM config file is located at /etc/openuem-server/openuem.ini. If you failed to provide the right setting while configuring OpenUEM you can edit this file to fix some settings.
This configuration file contains the database password and JWT secret in clear, as it’s needed for OpenUEM components, but please do note that the configuration file can only be read by the openuem user.
1.3.3 Certificates
Certificates used by OpenUEM should be located at /etc/openuem-server/certificates.
There’s a folder for every required certificate type or, more specifically, for every component type.
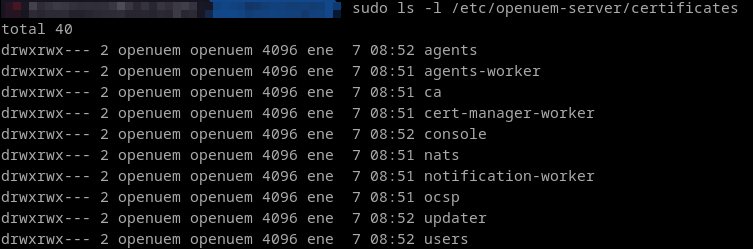
Just in case, you’ll find the administrator certificate in the users folder.
1.3.4 Logs
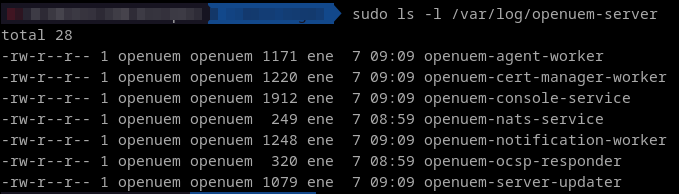
OpenUEM logs are stored in /var/log/openuem-server and you’ll find a log for every OpenUEM component that has been installed on that server. You’ll need root privileges to see the logs content.
1.3.5 Reinstalling OpenUEM
If you need to reinstall OpenUEM please proceed like this:
- If you want Debian/Ubuntu to ask you the configuration questions again, please use
apt purge openuem-serverto uninstall and forget the answers. Otherwise, useapt remove openuem-server - Drop OpenUEM database tables so the new installation can perform a clean installation of the schema. If you prefer to keep the database, at least remove the user’s table as OpenUEM creates an entry for the admin user’s certificate and that entry must be unique.